SHOULD MANUFACTURING ENTERPRISES CHOOSE MES OR ERP?
MES and ERP are two modern management systems designed to optimize production processes, inventory management, and various operational aspects. However, each system has its own strengths and weaknesses. Viettel Software will help managers better understand the features, benefits, and limitations of each solution, enabling them to make the most suitable decision for their manufacturing enterprise.

ERP System: Optimizing Resources and Enterprise Management
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a multifunctional integrated solution designed to consolidate and monitor all business operations across different departments within an organization.
The primary role of ERP is to centralize and synchronize information from various departments onto a single platform, enabling businesses to manage effectively and respond flexibly to requirements. ERP encompasses every aspect of a company’s operations, from financial management, order processing, and production, to supply chain management, inventory control, human resources, and customer relations.
Additionally, ERP helps standardize processes, automate business tasks, reduce manual errors across departments, and provide managers with a comprehensive view of the current business situation. With its ability to seamlessly connect production activities with related departments, ERP not only optimizes costs and enhances work efficiency but also improves customer service, thereby enhancing customer experience and satisfaction.
Functions
ERP synchronizes and aggregates all information and data from various departments and units into a single platform for monitoring, analysis, and responding to the business’s needs. An ERP system encompasses all of the company's activities, including modules like:
-
Financial Accounting
-
Human Resources
-
Architecture
-
Project Management
-
Data Services
-
CRM
-
Procurement System
-
Access Control System
Objectives
-
Support the connection of all production activities with related departments in the enterprise.
-
Optimize costs.
-
Improve labor efficiency.
-
Enhance customer service, thus increasing customer experience.
MES System: Optimizing the Production Process
The Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a critical computer solution in the manufacturing industry that helps track and record the entire process of converting raw materials into finished products.
Key Functions of the MES System
MES provides detailed information about the current status of the factory, assisting managers in making optimal decisions to improve production efficiency. Operating in real-time, MES monitors and checks various factors in the production process, including raw material inputs, personnel, machinery, equipment, and supporting services.
The primary goal of MES is to optimize production operations and increase labor productivity by collecting data, processes, and production outcomes, creating detailed records for every stage. The MES system includes features such as:
-
Product formulation management (assembly/processing recipes, raw material management)
-
Production planning and execution
-
Production resource management (machinery, equipment, capacity, etc.)
-
Coordination of production resources and tools (production/work orders)
-
Production progress reporting
-
Production batch tracking
-
Quality control
Thus, while ERP serves as the overall management system for a business, MES focuses on driving efficiency and quality within the production process.
Benefits of the ERP System for Businesses
ERP is a strategic tool that helps businesses improve operational efficiency and management by integrating business processes and optimizing resource usage. By implementing ERP, businesses can gain deeper insights into their operations, manage resources effectively, and plan for the future.
Some of the key benefits that ERP brings to businesses include:
-
Comprehensive Connectivity: Integrates departments on a single platform, enabling real-time management.
-
Error Reduction: Automates data entry processes, reducing errors from manual operations and enhancing work productivity.
-
Enhanced Customer Service: Optimizes processes and data to improve the customer experience.
-
Smart Access Control: Allocates access rights, preventing unauthorized document modifications, and enhancing information security.
-
Improved Collaboration: Enhances coordination between internal departments, as well as with suppliers and customers.
-
Standardized Processes: Optimizes operational processes, helping to reduce costs.
-
Remote Management Support: Provides tools to manage the business from anywhere.
-
Quick Decision-Making: Provides timely information for managers to make decisions based on real-time data and current business conditions.
Benefits of the MES System for Businesses
MES is a crucial tool that focuses on managing and optimizing the production process. By providing accurate real-time data, MES helps managers plan and monitor production lines while leveraging various benefits:
-
Error and Cost Reduction: MES helps minimize errors during production, cutting unnecessary costs and saving time.
-
Problem Diagnosis: When issues arise, MES enables quick identification of the cause, helping businesses resolve problems promptly.
-
Automated Data Entry: Reduce manual data entry tasks, increasing the efficiency of production-related departments.
-
Optimized Production Processes: Shorten production cycle times, increases efficiency, and optimizes capital utilization.
-
Efficient Equipment Use: MES supports the maximization of equipment and machinery utilization.
-
Reasonable Production Scheduling: Optimize production scheduling and raw material procurement to ensure maximum efficiency.
-
Reduced Product Defects: MES helps reduce the frequency of defective products, ensuring high-quality output.
Although MES focuses entirely on the production process, it does not directly connect with other departments like warehouse management, financial accounting, or customer relations management. For example, MES can notify you when a product is ready for shipment but does not automatically handle invoicing or update customer records.
To integrate production data with business activities like sales, procurement, customer care, and finance, businesses need to use an ERP system.
Comparing ERP and MES
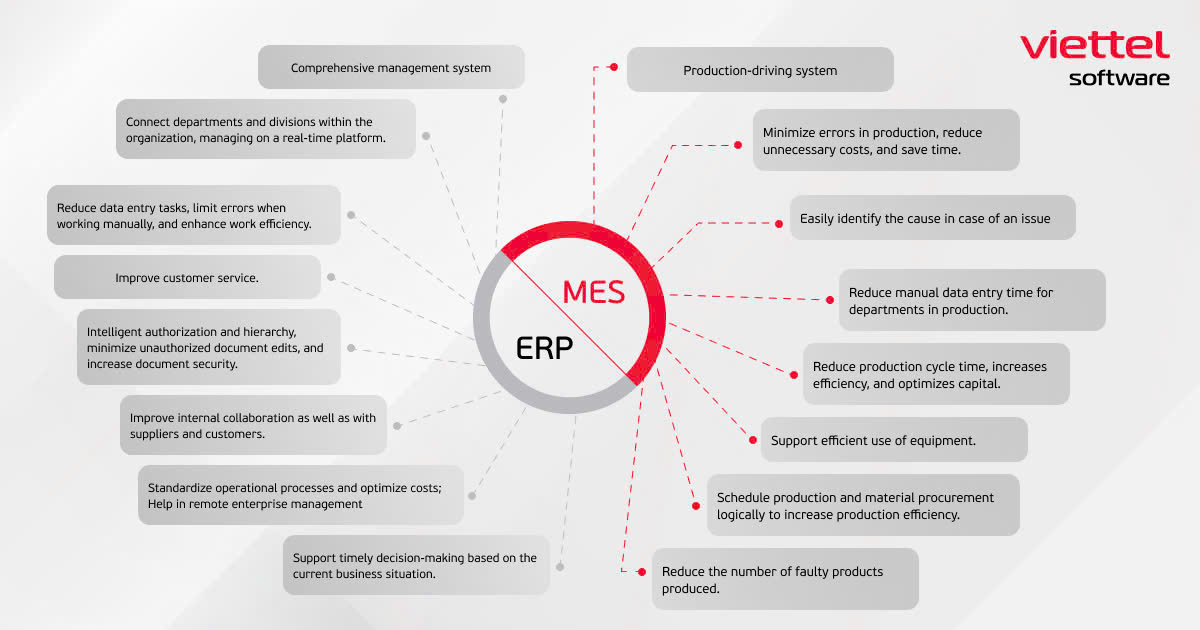
Both MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) offer distinct benefits and challenges, depending on the specific needs and business situation. Selecting the right solution is crucial for optimizing operations and achieving business goals.
Before deciding on implementation, managers should thoroughly understand the features and applications of each system. This understanding will provide a solid foundation for making an informed choice, ensuring the selected solution meets the business's requirements and objectives.
Fundamental Differences
The fundamental difference is that ERP controls the entire process and resources of a business on a single platform, providing an overall view. In contrast, MES controls each activity to optimize the production process in real-time, supporting operational decision-making and executing production processes throughout the factory.
Which System, ERP or MES, is More Suitable for Manufacturing Businesses?
Both systems have advantages and disadvantages depending on the company's needs and challenges. Sometimes, complex challenges require the combined use of both systems. Therefore, before making a decision, managers need to carefully assess the needs of their business.
ERP is more suitable when:
-
The business has multiple branches or workshops with common production processes.
-
The business needs to manage multiple departments and areas beyond production.
-
The manager requires an overview analysis and evaluation of the entire company or faces challenges in overall management.
-
The business experiences significant issues in internal operations.
MES is more suitable when:
-
The focus is on mass production or continuous manufacturing.
-
The business needs stringent product checks starting from raw material inputs.
-
Each factory or workshop of the company has different processes.
-
The business requires close monitoring, inspection, and maintenance of machinery and equipment.
We hope that the above comparison and analysis can help businesses make informed decisions when considering MES and ERP.
If your business needs to implement these systems or requires further consultation on other IT services from Viettel Software, please contact our Hotline at (+84) 988 889 446 or email us at contact@viettelsoftware.com.




